|
Research Title/
Graphical Abstract
|
Article Information /
Abstract
|
Download
|
|
Retrospective Study of Maternal age and Birth Weight in Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University Teaching Hospital (ATBUTH) Bauchi State, Nigeria

|
Original Research, D1
Umar A., Barnabas D., Murtala M.J and Ismaila A.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 01-04, 2014.
ABSTRACT: A cross-sectional retrospective study was conducted to determine maternal age and birth weight status of the newborn babies from April 26, 2005 to October 13, 2009. A total of 9,647 populations of newborn babies and their respective mother’s age were copied into a data sheet form from maternity record of ATBUTH, Bauchi State. This is a hospital located in Bauchi metropolis that serves the needs of individual belonging to the lower socio-economic groups. This study was done to determine the mean birth weight, incidence of low birth weight and sex ratio of live term deliveries at ATBUTH, Bauchi. The mean (SD) maternal age for male and female newborns were 25.56(6.91) and 25.63(6.94) respectively. And for the mean (SD) birth weight was 3.14(0.57) for male newborns and 3.09(0.57) for female newborns. It was found that male infants were 50g heavier than female infants. The present study found that caesarean section (CS) is higher in babies with a mean (SD) birth weight of 3.21(0.66) and above, while spontaneous vaginal delivery (SVD) is at mean (SD) birth weight of 3.11(0.57) among people attending maternity ward of ATBUTH, Bauchi. Furthermore, difference in mean birth weight was statistically significant in case of sex (p<0.001). The sex ratio of the present population study was found to be 0.99, which means more female newborns than males. Emphasis on health education and promotion programmers to encourage late (non teenage) motherhood and discourage early pregnancies among individuals and also inform all the women during antenatal visits about the consequences of low birth weight and significance of delivering the babies with normal birth weight is recommended.
Key words: Maternal age, Birth Weight, ATBUTH, Nigeria
|
 |
|
Change as a Necessity in Medical Education: Let’s Review its Main Limitations and Know “Adaptive Reflection” Approach as a Change Facilitator

|
Original Research, D2
Arab M., Ahmady S. and Yaghmaie M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 05-08, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Background: Change in medical education should be considered as a necessity. Material and methods: change management and its difficulties are described in medical education.Results:”Adaptive Reflection” approach as an outcome-based model is introduced in the present study. Main attentions of the model are emerging adaptation and learning, concept of change, motivation, anxiety, uniqueness of context, empathy and change of managing method. Conclusion: Conventional defreezing-change-refreezing model should alternate to new approach including different understanding of change management.
Key words: Change, Medical Education, Reform, Learning
|
 . .
|
|
Effect of 8-week in-place and Transitional Training on Obese Young Men's Body Composition and blood Lipid Profile

|
Original Research, D3
Azadi B., Bolboli L., Khani M. and Sadri K.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 09-14, 2014.
ABSTRACT: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of in-place (exercise bike + weight training) and transitional (jogging + dynamic exercise) training methods on body composition and blood lipid profile of young obese men. Participants of this study were 40 young obese (BMI>30) men (Age: 29.00±1.16, Height: 174.85±3.21, weight: 108.56±3.45) which randomly divided in to two groups of in-place and transitional training. Then, subjects did an 8-week transitional or in-place training program, three sessions a week, 75 minutes a session. Before and after intervention, body composition and blood lipid profile of the subjects has been measured. Data were analyzed using paired and independent t-test in the significance level of 0.05 under SPSS software (version 17). Findings showed that both in-place and transitional trainings had significant effect on the reduction of fat mass and improving lipid profile of blood in young obese men (p <0.05) and there wasn’t significant difference between the effect of two training methods. According to the findings of this study, it seems that both transitional and in-place training methods have sufficient efficiency for reduction of fat mass in obese men if training principles are considered properly. But, for obese people and those who are suffering from injuries in lower limb or don’t have tolerance for increasing heart rate and breathing problems, it is suggested to use in-place training for improving body composition and controlling weight. Because, this kind of training can help reducing fat mass and improving lipid profile like transitional training and is more tolerable.
Key words: BMI, Fat Mass, in-Place Training, Lean Body Mass, Lipid Profile, Obesity, Transitional Training
|
.
|
|
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis

|
Original Research, D4
Negahi A., Golmirzaei J., Hamedi Y., Shahrzad ME., Zare Shahri R. and Namazi SSH.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 15-20, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Comorbidity of multiple sclerosis (MS) and depression is documented in several studies. The aim of present study was to evaluate the prevalence of depression among patients with MS and associated factors. This cross sectional study was carried out in Bandar Abbas in 2013. Totally 106 patients were enrolled by convenience sampling and were ask to complete the Persian version of Beck depression inventory (BDI). Each questionnaire pointed between 0 and 63 scores. Patients who achieved less than 8 scores, considered as healthy. Those pointed between 9-18, 19-29, 30-40 and above 40 scores considered as, mildly, moderately, severely and very severely depressed patients respectively. Demographic data of patients and their drugs information collected. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics indices such as mean, standard deviation, frequency and statistical test including independent sample t-test, chi-square, ANOVA and Pearson’s correlation. P-value less than 0.05 considered statistically significant. The mean age of participants was 33.58 ± 8.3 (ranged 18-54 years). Among the participants 31 subjects (29.24%) were healthy and 30 (28.3%), 28 (26.41%), 15 (14.15%), 3 (2.83%) patients were mildly, moderately, severely and very severely depressed respectively. Prevalence of depression among females was two times higher than females (T= -2.16, p-value = 0.033, 95% CI: -9.65_ -0.42). Also, depression was significantly higher among those with lower income and unemployed patients. Prevalence of depression among MS patients in Bandar Abbas was comparable with other studies. Direct interview with an adult psychiatric in order to predict the accurate depression prevalence is recommended.
Key words: Prevalence, Mood Disorders, Depression, Multiple Sclerosis
|

|
|
Echium Amoenum Fisch. Et Mey: A Review on its Pharmacological and Medicinal Properties

|
Original Research, D5
Abed A., Vaseghi G., Jafari E., Fattahian E., Babhadiashar N. and Abed M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 21-23, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Echium amaenum, famous as Borage, belongs to Boraginaceae family. It grows widely in most of Europe, Mediterranean region and also found in northern parts of Iran. It is one of the famous plants in Iranian traditional medicine for different kind of effects such as demulcent, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic and sedative properties. The main medicinal parts of the plant are flowers and the leaves. The plant consists of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), alphalinolenicacid (ALA), delta6-fatty acryl desaturase, delta8-sphingolipid desaturase, pyrrolizidine alkaloids, and mucilage, resin, potassium nitrate, calcium and mineral acids. This review focuses on pharmacological properties of Echium amaenum as antibacterial, antioxidants, analgesic, anxiolytic, antidepressant, immunomodulatory, protective effects on pancreatitis and antiviral agents.
Key words: Echium Amoenum, Boraginaceae, Family anti-inflammatory
|
.

|
|
The Impact of Cigarette Packaging Health Warning Labels On Smokers in Bandar Abbas, south Iran

|
Original Research, D6
Asadian A., Aghamolaei T., Madani A. and Ghanbarnejad A.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 24-29, 2014.
ABSTRACT: One of the principal methods for informing tobacco consumers about the risks of smoking is the warning message on each cigarette package. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect warning labels cigarette on smokers. This cross-sectional was conducted on 300 male smokers residing in city Bandar Abbas, south Iran, in 2013.Subjects cluster random sampling from 10 urban districts. Data collection tools included demographic characteristics, attitudes, reaction and pattern of smoking on smokers. The collected data was analyzed by SPSS software19 and descriptive and inferential test. The mean age of smokers was 36.8 years with a standard deviation of 9.9 and range varied from 18 to 70 years. The mean history of smoking was 13.6 years and average number of cigarettes smoked daily was 13.3. Respectively terms of education, most of smokers had a high school diploma. Descriptive statistic revealed 2 percent poor, 44 percent moderate and 54 percent of smokers had good attitude towards health message. 44 percent of smokers had good reaction (notice, talk about messages, reminders, disgust, and fear) to health warning message. Chi-square test showed a significant relationship (P < 0.001) between smokers, reaction to health messages and their attitude. Smokers have a good attitude to messages, their attention was drawn to the message, when smoking messages were remembered and talked about the messages and messages leading to fear and hate them of smoking. Based on the results, it is suggested to strengthen features such as attract attention, raising awareness, remember effects of smoking, thinking about the effects of smoking, raising concern, fear and hate in health warning message on cigarette packages that response to the message and will be followed to reduce smoking.
Key words: Health Warning Labels, Attitude, Reaction, Smoking
|
 . .
|
|
Prevalence of Anterior Knee Pain in Patients with Tibia Fractures Post Intra Medulary Nailing
|
Original Research, D7
Emami Moghadam Tehrani M., Amuzadeh Omrani F., Manafi Rasi A., Khani S. and Ebrahiminia M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 30-32, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Tibia and fibula are most common places of fractures in lower limbs caused by high energy traumas. There were many treatments for these fractures so far, Intra Medulary Nailing is one of the most important treatments with complications such as anterior knee pain, neurovascular injury and nail fracture. Anterior knee pain is the most common complication. This is a prospected cross sectional study on patients with tibia fracture referred to Shahid Rajaei Hospital, Tonekabon and Imam Sajjad Hospital in Ramsar in 2011, treated with IMN. Data collected, including demographics, knee pain and ability to squat 1 and 3 months after operation. They were analyzed with SPSS 18.0. P<0.05 was considered as significant. A total of 80 patients participated in this study that 46.3 percent of them aged between 20 to 30 years old. Anterior knee pain was seen in 86 % and 75 % and difficult squatting was seen in 91 % and 73 % of patients, one and three months after surgery, respectively. This study showed that anterior knee pain is a common complication of IMN therapy. Retrospective and prospective studies are needed for more general results.
Key words: Knee Pain, Lysholm, Intra Medulary Nailing, Squatting test.
|
 . .
|
|
Study of Calcaneus Bone Densitometry in Post-Menopausal Women

|
Original Research, D8
Manafi Rasi A., Amuzadeh Omrani F., Kazemian GH., Ebrahiminia MR. and Khani S.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 33-34, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Osteoporosis is one of the most common age related diseases, especially in post-menopausal women who may have higher prevalence and risks of complications as fractures. The aim of this study is to determine average T-score and Calcaneos bone densitometry in post-menopausal women. It is a cross sectional study conducted on post-menopausal women aged between 40 to 60 years old who had been admitted to orthopedic ward of the Shahid Rajei Hopspital, Tonekabon, 2011. We used quantitative ultrasonography (QUS) of heel bones in Calcaneus bone densitometry. Data were analyzed by SPSS 20. We considered P<0.05 as significant.A total of 50 women aged between 40 to 60 years participated in this study. Thirty five patients (70%) were osteoporotic and 15 patients (30%) were healthy. Fourteen patients (28%) of those with osteoporosis, had age of menopause, less than 5 years and 21 (42%) more than 5 years. No significant relationship was found between the mean T Score and the menopausal years (p <0.01). This study showed that there is a significant relationship between Calcaneus bone loss and postmenopausal osteoporosis. Given the high prevalence of post-menopausal osteoporosis and its high costs of health care and long-term treatment, the need for comprehensive studies of screening and early detection, prevention and early treatment is recommended.
Key words: Calcaneus, Densitometry, T-Score, Osteoporosis, Post menopause.
|
 . .
|
|
The Response of Blood Buffering Capacity to Three Types of Recovery during Repeated High-Intensity Endurance Training

|
Original Research, D9
Fashi M., Kazemi K., Sheikhani Shahin H., Khani M. and Rostamzad K.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 35-39, 2014.
ABSTRACT: The aim of this study was to determine the response of chosen parameters of blood buffering capacity to three types of recovery during repeated high-intensity endurance training. Ten physical education students studying at Kharazmi University of Tehran participated in this study. They performed repeated high-intensity endurance test (RHIET) in each session. The RHIET consists of four bouts about 2:30 minutes. Recovery periods of 5minutes were allowed between bouts. RHIET differed in the kind of activity performed during the recovery periods; Gouging at 63% maximum heart rate, stretching exercises and lying down in supine position. A sample of 5CC arterial blood obtained from each individual immediately after the last recovery period. Blood sample were sent to the laboratory for homology test. Their buffering capacity was measured by assessment of the following parameters: pH, HCO3–/CO2, buffer base (BB), base excess (BE), O2-sat, PO2. The ANOVA Repeated-Measures was use to analyze the data by SPSS 17. Significant differences were shown between the active recovery and the stretching exercises recovery and between the passive recovery and the stretching exercises recovery on pH, BB and between active recovery and the passive recovery on O2-sat and PO2 (P≤0/05). There were no significant differences between the active, passive and stretching exercises recovery on HCO3–/CO2, PCO2 and IS (p≤0/05). Therefore, this study showed that the passive recovery improve buffering capacity compared to the stretching exercises and the active recovery. It could be also hypothesized that increased alveolar gas exchange with passive recovery can due to slower heart rate and slower breathing rate; the kidneys removal of H+ and HCO3- reabsorption; decreased metabolism and metabolic products, Whole body temperature (muscle, blood), and strongly oxygen binding to hemoglobin. Hence, pH will increase and buffering capacity will be improved.
Key words: Recovery, Repeated High-Intensity Endurance Training, Blood Buffering Capacity
|

|
|
Relation of Anxiety, Sleep Disorders and Drug Abuse with Patient’s Tendency Toward Sedative Drugs in Semnan Prison

|
Original Research, D10
Haghighat M., Tabatabaee S.M. and Rahimian Boogar I.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 40-45, 2014.
ABSTRACT: According to statistics and reports, excessive use of sedatives can lead to serious illness or even death. Taking sedatives is rising among the prisoners. Investigating the possible causes of this drug use and finding alternatives to minimize it is an important issue that needs professional attention, whether in the field of medical science or in the realms of psychology. This study aimed to investigate the relationship of anxiety, sleep disorders and drug abuse with sedative drugs in male patients of Semnan prison. Due to the lack of population, all sedatives users of Semnan prison were considered as sample. A list of names was prepared with the assistance of prison physician. Participants in this study responded to Pittsburgh Sleep Disorders (The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index), Spiel Berger State-Trait Anxiety questionnaires and a five-choice question for assessment of drug abuse. The results showed that there is a relationship between anxiety, sleep disorders and taking sedatives. But there is no relationship between drug abuse and taking sedatives.
Keywords: Sedative, Drug Abuse, Sleep Disorders, Anxiety.
|

|
|
Baobab Fruits (with\without Shell) Affected by Wrapping and Type of Packaging Materials During Storage Period

|
Original Research, D11
Adam Eldoom E., Elmubarak Ali A. and Awad Abdel-Razig K.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 46-52, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Baobab fruit pulp is derived from the fruits of the Baobab tree (Ad Ansonia digitata), also known as the 'upside down tree 'The applicant proposes to market a baobab fruit pulp as a novel food ingredient for use in a range of food products namely beverages, smoothies, cereal bars and other similar food products. In this study baobab fruits pulp was analyzed for proximate composition and effect of wrapping material on fruits during storage. Seventy seven samples of raw Baobab fruit as well as market samples were studies for chemical composition. Moisture content%, pH, treatable acidity %, TSS, Ascorbic acid content ml/100g, total sugars content%, Reducing sugars content% and ash content % were evaluated ,the pulp contain substantial quantities of treatable acidity 6.30%, TSS 7.00, total sugars 13.00%, Reducing sugars 5.70% and high amount of Ascorbic acid content (392.00 mg/100g of fruit pulp). Baobab contains naturally dehydrated fruit pulp, which contains five times or more the vitamin C content present in oranges (53mg/100g of fruit pulp). The study proved that packaging materials have a significant impact in reducing the nutritional value generally and vitamin c in particular. The study revealed that Poly ethylene bags the best one.
Key words: Baobab, Dehydrated Fruit Pulp, Vitamin C.
|

|
|
Evaluation of prostasin Levels in serum of patients with ovarian cancer as a new potential Tumor Marker

|
Original Research, D12
Heidari M., Bastani A., Asgary A. and Malekkandi M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 53-57, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Prostasin has been considered as a new biomarker with high sensitivity for ovarian cancer diagnosis. This study aims at evaluating the changes in levels of serum prostasin biomarker in patients with ovarian cancer and determining the efficacy of this biomarker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer. This descriptive-analytical study was performed on women with ovarian cancer. The serum levels of prostasin and CA125 were measured using ELISA and Electrochemiluminescence techniques. The data was analyzed using SPSS Ver. 11 and the level of statistical significance was considered to be p < 0.05. Totally, 110 subjects participated in this study, including 20 patients with malignant ovarian tumors, 66 patients with benign tumors and 24 healthy women. A significant increase in serum prostasin and CA125 levels was observed for malignant group comparing with the control group and the people with benign tumors (p < 0.05). The cut-off point, sensitivity and specificity of prostasin in diagnosis of ovarian malignancies compared with ovarian benign tumors and the control group were 9.3 μg/ml, 0.89 and 0.75, respectively. These levels were reported for CA125 in diagnosis of ovarian malignancies, ovarian benign tumors and the control group as 35.17, 0.85 and 0.75 U/ml respectively. The findings of this study show that prostasin can serve as a good biomarker for ovarian cancer diagnosis with suitable sensitivity and specificity. Further studies are required to generalize these findings.
Keywords: Cancer, Ovarian tumor, Marker, Prostasin.
|

|
|
The Comparison Efficacy of Montelukast and Echinacea as Decreasing the Incidence of Common Cold
 
|
Original Research, D13
Mohammadi K,, Safdarian F., Zare SH. and BagherRahmati M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 58-61, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Common cold is the most common infection in children before the school aged and costs a lot yearly. The aim of doing this research is to evaluate the influence of montelukast and Echinacea in reducing the incidence of common cold between the children in 1 to 5 years old that refers to Bandar Abbas hospital. In this study, 100 healthy children between 1to 5 years old, without any heart and lung disease were selected. The children were distributed into two groups. One group was assigned to receive Echinacea syrup (Imogen) 1cc daily and another received 4 mg muntelukast daily during 8 week. A questionnaire included age, sex, the number of catching cold, sinusitis, otitis media, pneumonia, was applied during 8 week. Parents called immediately after any sign and children were examined. Data was analyzed by SPSS19 software. Using descriptive statistics for demographic data and Chi-square Test with Fisher's exact test for Statistical Analysis. Between 100 healthy children that were studied, the average age of Echinacea group was 2.5 years and the muntelukast was 3.1years.The rate of boys to girls was 2:1.In both groups there wasn't any meaningful difference in age and sex. In group that was received Echinacea, from 50 children 17 didn't get cold at all (34%), while in other group only 3 people didn't get cold at all. Meanwhile 19children get cold 2 times. The average of getting cold in group of Echinacea received was one time and in other group was 2 times. In this study, it is obvious that Echinacea syrup in compare with montelukast reduces the incidence of getting common cold in children between 1 to 5 years old. But there is no influence in reducing the complication of cold. Nothing drug reaction was reported during the use of these medications. With a larger study and using placebo with these drugs and with a double blind study could receive more useful information in preventing common cold can be received.
Key Words: Montelukast, Echinacea , Common Cold, Prophylaxis
|

|
|
Comparative Study of the Effects of Mental, Physical and Combined Exercises on the Reactions of Students with Visual Impairments

|
Original Research, D14
Ahmadi Barati A., Yousefi I., Ghaini S., Ahmadi S. and Behpour N.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 62-67, 2014.
ABSTRACT: The purpose of this quasi-experimental study was to compare the effect of the combination of mental and physical exercises on the reaction of the students with visual impairments. The subjects were 30 girls of 9 to 12 years old who had congenital blindness and were selected by the available sampling method and randomly divided into three groups of 10 mental exercise, physical exercise and combined exercise. Experimental work of the groups was 8 two sessional weeks in time duration of 45 to 60 minutes per session. Subjects' ability to react was measured through ruler testing. Statistical analysis of the data was done using descriptive statistics, one-way ANOVA, LSD post hoc test and paired t-test at a significance level of P<0.05. The results indicate the significant superiority of mental exercise techniques (24.1±7/7) relative to physical exercise (30.2±9.5) and combined exercise (28.6±8.9). According to these findings, the physical education teachers of blind children while working to develop the capabilities of their student’s rate should benefit from specialized mental exercises in the components related to the reaction.
Key words: Mental Exercise, Physical Exercise, Mental - Physical Exercise, Reaction Capability, Visual Impairments
|

|
|
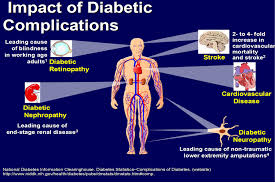
A Study on the Prevalence of Diabetic Complications in Fasa Diabetes Clinic
|
Original Research, D15
Ghodsi R., HamayeliMeharbaniH., AvandA.Q., Bordbar A. and Ahmadzadeh S.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 4(1): 68-72, 2014.
ABSTRACT: Diabetes is a chronic disease with increasing prevalence which its treatment have a high cost and burden of disease. This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of diabetes complication in the patients referred to Fasa diabetes clinic. This was a cross-sectional study from March 2009 up to September 2013 among 1131 referred diabetes patients. Anthropometric and demographic data were gathered, type of diabetes, duration of disease, blood pressure, serum glucose and lipid profile were measured. Chronic complications including neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, cardiovascular disease and diabetic foot were recorded based on the physician reports. Mean±SD of age for diabetic patients was 51.8±12.9, less than one percent had gestational diabetes, 2.8% were diagnosed by type I diabetes and 96% had type II diabetes mellitus which 15.2% of them used insulin therapy, 81.1% oral hypoglycemic agents and 2% followed a dietary plan. More than one third of subjects had uncontrolled hyperlipidemia or hypertriglyceridemia. Neurologic and cardiovascular diseases were the most prevalent complications between diabetes patients; 33.8% and 26.8%, respectively. The prevalence of diabetic foot was 2.4%. The high prevalence of diabetic complications was considerable in Fasa diabetes patients. The lack of control for risk factors such as cholesterol, triglyceride, blood sugar and blood pressure make quality of treatment a major concern in Fasa.
Keywords: Diabetes, Prevalence, Complications
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|