|
Research Title/
Graphical Abstract
|
Article Information/
Abstract
|
Download
|
|
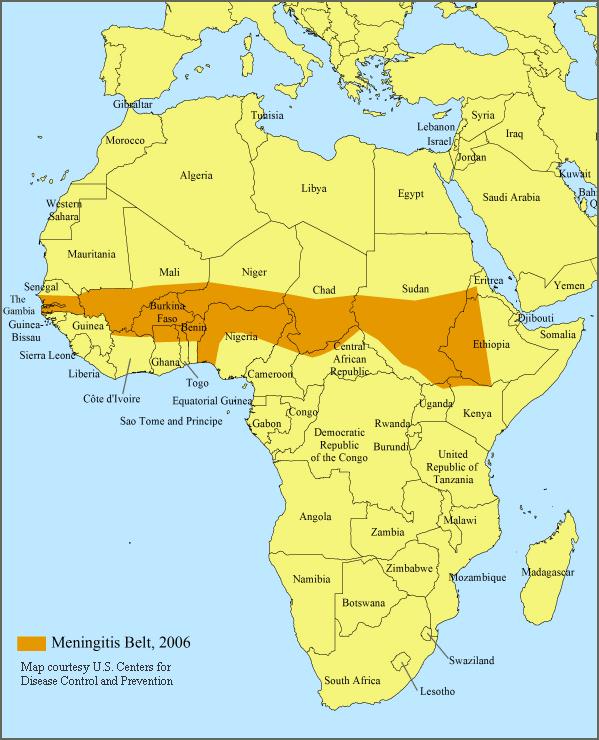
Weather Variables and Climatic Influence on the Epidemiology of Cerebrospinal or Meningococcal Meningitis
|
Original Research, C1
Obiakor, M.O.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 3(1): 01-10, 2013
ABSTRACT: Meningococcal infection has been recognized as a serious problem for almost 200 years. Cerebrospinal or Meningococcal meningitis (MCM) can occur as a sporadic case, institution based focal outbreak, or a large epidemic year. The distribution of serogroups causing meningococcal disease (A, B, C, Y, W-135) varies over time and by geographic location and spatial distribution of the disease indicate close linkage of it and weather climatologies. The highest burden is in sub-Saharan Africa, where it occurs in a cyclic mode. The paper while drawing facts on the disease history, African Meningitis Belt, causative agents, disease statistics, risk factors, and overall etiology, compares the information on cases and deaths of MCM from various literature reports, noted the linkage between regional climate variability/ seasonal variation and MCM. Efficient management of the risks of cerebrospinal meningitis requires a multi-sectoral approach, which brings information about how climate interact with the various elements of society, environment and economy. Strong partnerships and high-quality data are needed from all sectors involved. Climate services, that include climate advisories, predictions, warnings and alerts, could also help societies take advantage of the opportunities associated with climate events.
Keywords: Region, Weather variability, Meteorology
|
 |
|
Investigation of In-vitro Anthelmintic Activity of Aqueous And Ethanolic Extracts of Leaves And Seeds of Guizotia abyssinica (L.F.) Cass

|
Review Article, C2
Dwivedi S, Kohli S, and Dwivedi S.C.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 3(1): 11-13, 2013
ABSTRACT: The aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Guizotia abyssinica (L.f.) Cass. were evaluated for anthelmintic activity using adult earthworms. The leaves and seed extract exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition of spontaneous motility (paralysis) and evoked responses to pin-prick. With lower doses the effects were comparable with that of albendazole. However, there was no final recovery in the case of worms treated with aqueous extract of seeds and ethanolic extract of leaves. The result showed that these extract possessed wormicidal activity and thus, may be useful as an anthelmintic agents.
Keywords: Guizotia abyssinica, Leaves, Seed, Anthelmintic activity
|

|
|
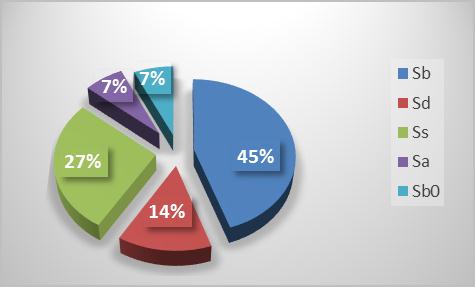
Evaluation of Respiratory Function Test in Children with Sickle Cell Anemia with Acute Chest Syndrome
|
Original Research, C3
Molavi M and Doozandeh H.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 3(1): 14-17, 2013
ABSTRACT: Sickle cell disease is caused by mutant recessive autosomal in β-globin chain leading to deformation of sickle cells. Hemoglobin S in deoxygenated conditions causes microvascular obstruction and adverse effects on various organs. The manifestation of sickle cell in lungs is as a thromboembolism, acute chest syndrome and abnormal lung activity test. This study aimed to Evaluation of the respiratory function test in children with sickle cell and its relationship with age, sex, allele type, acute chest syndrome and pain crisis, that lung injury of these patients to be diagnosed early. This descriptive-analytical study was done on 6-18 years old children in the Pediatric Hematology Clinic at Bandarabbas Hospital in 2011 to 2012. Following the CBC, Hb electrophoresis, spirometery and records of the patients (acute chest syndrome, pain crisis), theses date were recorded and imported to SPSS20 statistical software (mean ± SD) and analyzed by Chi-squar test. Of 29 patients, 17 were male and 12 were female. Highest genotype was SB 44.8 % (13 cases) and lowest was SA and SB0 6.9 % (2 cases). Results of lung function test were as follows: restrictive pattern (72.4%, 21 cases), normal pattern (20.7%, 6 cases) and obstructive pattern (6.9%, 2 cases). There was no significant difference in pattern of pulmonary function test in patients with and without history of previous acute chest syndrome. There was also no significant correlation between spirometric pattern and age, sex, type allele and pain crisis. Pulmonary function is abnormal in 79.3% children with sickle cell anemia. Common abnormalities include restrictive pattern.
Key words: Sickle Cell Anemia, Lung Activity Test, Acute Chest Syndrome
|

|
|

Hot Paper
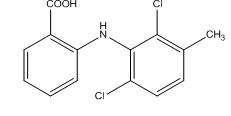
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Quercetin-Meclofenamic acid Conjugate: A Mutual Pro-drug for Safer NSAIDs
in terms of careful work, write and submission
|
Original Research, C4
Gupta K. and Kulkarni AP.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 3(1): 18-23, 2013
ABSTRACT: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most commonly used medications worldwide for the treatment of pain, fever and acute, chronic inflammatory diseases like arthritis. Although they are effective in the treatment of pain and inflammation, their routine and long-term administration is limited due to their gastrointestinal and renal side effects. Most of the natural constituents, polyphenolic compounds and flavonoids, possess potent anti-inflammatory effect and fewer side effects. They may be used as the potent anti-inflammatory agents; however, they suffer from the bioavailability problems. The present study attempted to synthesize a conjugate of quercetin and meclofenamic acid, on the basis of the merits and demerits of both of these compounds. The conjugate and the intermediates were characterized by determining melting point, Rf value by Thin Layer Chromatography, UV Spectrophotometry, Infrared Spectra, MASS by L.C.M.S. The anti-inflammatory activity of the conjugate was compared with quercetin and meclofenamic acid by animal study. The probable mechanism of action for the synthesis was discussed. The in vivo activity of the conjugate quercetin-meclofenamic acid significantly inhibited paw edema in the first and second phase, suggesting an inhibitory effect on the release of histamine, serotonin, kinins and prostaglandins. The improved pharmacological activity may be contributed to aqueous solubility and comparatively lesser molecular weight of the conjugate. In conclusion, a mutual prodrug quercetin-meclofenamic acid, associated with anti-inflammatory activity, was successfully synthesized and characterized.
Keywords: Mutual prodrug, Quercetin, Meclofenamic acid, Anti-inflammatory, Natural Compounds
|

|
|
Effect of Different Packaging Materials on Microbiological Quality of Baobab Fruit Pulp

|
Original Research, C5
Eldoom Adam E.A, Elmubarak Ali A, and Abdel-Razig K.A.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res. 3(1): 24-27, 2013
ABSTRACT: Today, dried fruit consumption is widespread in developing countries such as Sudan. Traditional retain most of the nutritional benefits of fresh fruit, and gain others. Dried fruit contains a large amount of fiber, and it is widely accepted that eating a very high fiber meal, such as a large amount of dried fruit, can cause increased gas production and a shortened transit time of food through the intestines. This experiment was designed to try to determine if dried fruits contain heavy loads of bacteria or mold since these microorganisms might contribute to foodborne diseases sometimes experienced after ingestion. This study was conducted during March 2006 and March 2007 to understand the relationship between different packaging materials and loads of microorganisms. Different packaging materials namely jute, basket and polyethylene were used in this study. The sample of baobab fruit divided into two portions. In the first portion shells were removed while in the second portion shells were not removed. All samples were stored at ambient temperature (35Cº±5) sample from market was evaluated for comparison. The total bacterial load was determined by employing total plate count (TPC), pour plate (PP) and spread plate (SP). The highest load of bacteria was found in market sample. The predominant bacteria isolated from the samples were species of Staphylococcus, Bacillus, Listeria, E. coli, Vibrio and Salmonella. The fungus (Asperigillus) also isolated from samples and samples collected from market for comparison. The study revealed that contamination of shelling sample was shown in basket samples only. In sample that was stored without shell polyethylene sample was showed the highest TPC followed by jute and basket.
Keywords: Baobab Fruit, Polyethylene, Predominant Bacteria
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|