Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 7 (1); 25 March, 2017
Evaluation of Chronic Orofacial Pain in Dental Patients; A 10 Years Retrospective Study.
Rezazadeh F and Rahimi S. 2017.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(1): 01-05, 2017; pii:S2252043017000001-7
Abstract
This retrospective study investigated the data of 427 patients who had suffered from orofacial pain and were referred to Shiraz oral medicine department, Shiraz, Iran. The patients’ diagnoses, gender, age, treatment, response to treatment, pain duration, severity of pain and other items were extracted from the medical records in the past 10 years. Most of the patients were females and their mean age was 49.57. The main diagnoses were temporomandibular disease (43.9%) and neuralgic pains (27.8%). Most of the patients had suffered for more than 6 months from the pain onset. 47.2% showed remission or significant improvement and 27% did not respond to treatment. 55.5% of the patients had experienced a severe pain. In this population, a majority of patients had suffered from temporomandibular disease and neuralgia. The chronic pain was reported to be higher in middle aged females which means that age and gender can be considered as two risk factors.
Keyword: Orofacial pain, Epidemiology, Chronic pain, Dental patients, Clinical observation, Anesthesiology
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
Formulation and Evaluation of Glycyrrhizin Alginate Beads for Stomach-Specific Delivery.
Rathore M, Shriwas Sh, Dwivedi S and Dubey R.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(1): 06-08, 2017; pii:S2252043017000002-7
Abstract
Gastric irritation is a very common problem with various stomach related disorders. The present research was undertaken to formulate floating calcium alginate beads of glycyrrhizin for targeting the gastric mucosa and prolonging their gastric residence time. Glycyrrhizin is the chief sweet tasting active constituents of the plant Glycyrrhiza glabra which belongs to the family Fabaceae. Glycyrrhizin is used for the treatment of ulcer and also now-a-days used as natural sweetening agent. The beads were prepared by suspending glycyrrhizin in calcium alginate solution. The beads were prepared using calcium alginate and glycyrrhizin (1:1) and were evaluated. The mean diameter, drug loading and entrapment efficiency were evaluated. Thus, the present investigation aimed in formulating stomach specific drug delivery useful in the treatment of gastric problems.
Keywords: Glycyrrhizin, Calcium alginate beads, Stomach specific
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
Exploration of Ethnomedicinal Flora Used Against Various Human Ailments in Moist Temperate Himalayas of District Bagh, Azad Jammu and Kashmir.
Safeer S, Sarwar R, Ubaid-ul-Hassan, Khalil S and Farhan Anwar ShM.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(1): 09-15, 2017; pii:S2252043017000003-7
Abstract
Present studies have been carried out to access, document and describe the ethno-medicinal potential of three different sites of projected area. Structured, semi structured and open ended questionnaires as well as detailed oral interviews of local inhabitants were the methodology to gather valuable knowledge. A total of 34 ethnomedicinally important taxa belonging to 25 families were reported. Among them, 2 were Pteridophytes, 3 were Gymnosperms while the remaining 29 were Angiosperms. Asteraceae contributed a significant number of species (4 spp.), followed by Pinaceae (3 spp.), Ranunculaceae, Aracaceae, Violaceae and Poaceae (2 spp. each) while remaining 19 families represented single species. Regarding habit, 22 herbs, 7 shrubs and 5 trees were documented. Mode of administration of the medicinal flora was as, 27 plants were applied externally while 7 species had both internal and external applications. Majority of the reported taxa were used to cure multiple type of diseases e.g. 12 species for gastrointestinal disorders, followed by respiratory diseases (9 spp.), muscular malfunctions (6 spp.) and hepatic disorders (4 spp.). In addition, three plant species were used against skin problems, eye infections, fever and headache and urinogenital troubles, while two species each were used for cardiovascular and neruro malfunctions. Only one plant was used against snake bite.
Keywords: Himalayas, Ethno Medicinal, Taxa, Diseases, Habit, Flora
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
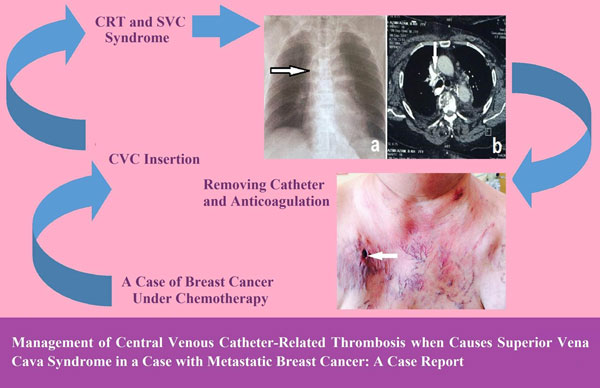
Management of Central Venous Catheter-Related Thrombosis when Causes Superior Vena Cava Syndrome in a Case with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Case Report.
Hejazi ME, Tahsini Tekantapeh S and Ghasemi F.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(1): 16-18, 2017; pii:S2252043017000004-7
Abstract
Today there is an increase in the use of central venous catheters in clinical practice. One of the dangerous complications of central venous catheters is symptomatic or asymptomatic thrombosis which sometimes causes superior vena cava syndrome. One of the most common causes of superior vena cava syndrome is malignant mass compression effect, also sometimes happens because of post thrombotic syndrome of central venous catheters. A 65 year-old woman was admitted to Imam Reza Hospital, Tabriz, Iran with superior vena cava syndrome. CT-Angiography demonstrated a massive filling defect in distal of superior vena cava adjacent to central venous catheters in favor of central venous catheters thrombosis. Central venous catheter-related thrombosis was successfully treated with therapeutic anticoagulation and catheter removal. As a conclusion, when central venous catheter-related thrombosis causes superior vena cava syndrome, despite the lack of consensus, therapeutic anticoagulation along with catheter removal are introduced as a successful way in central venous catheter-related thrombosis management. Based on the existing data found in previous studies about patients with central venous catheters, it can be claimed that a strong association exists between central venous catheter-related thrombosis presentation as a superior vena cava syndrome and malignancies. In patients with central venous catheter-related thrombosis who are presented with superior vena cava syndrome, successful clinical improvement is obtained by therapeutic anticoagulation along with catheter removal.
Keywords: Anticoagulation, Catheter removal, Central venous catheter, Post thrombotic syndrome, Thrombosis
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
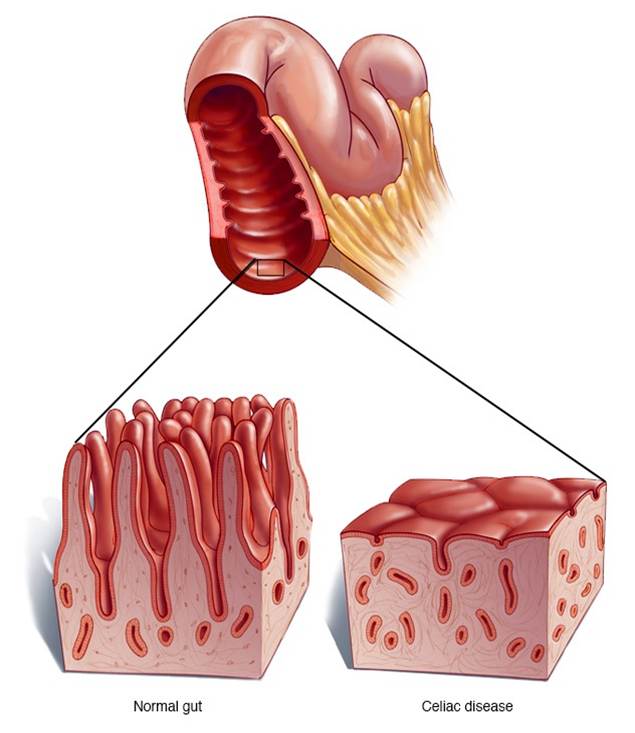
Evaluation of Tissue Transglutaminase IgA in Thalassemia Minor Patients.
Noori NM, Shahramian I, Teimouri A, Haghighat M, Dehghani SM and Sharafi E.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(1): 19- 24, 2017; pii:S2252043017000005-7
Abstract
Minor beta thalassemia is a common condition in children. The aim of the present study was the investigation of serum tissue transglutaminase IgA level as potential celiac disease in patients with thalassemia minor. This case control study was conducted on patients with beta thalassemia minor and healthy children in the years of 2014 to 2015. A total of 300 children were enrolled and IgA and tissue transglutaminase IgA levels were measured. The normal limit of tissue transglutaminase IgA was considered to be 20 IU/mL. Data analysis was performed using SPSS20 with 95% confidence of interval. Two groups of participants were matched regarding sex (Chi-Square = 0.436 and P = 0.509). Mean age of participants was 8.46 ± 4.54 and 7.74 ± 2.99 in minor and control respectively. Means of age, body mass index and serum tissue transglutaminase values were different between case and control while only serum tissue transglutaminase was significant (P=0.024). The status of tissue transglutaminase had a significant correlation with case and control (P<0.001). It is concluded that a positive association exists between β- thalassemia minor and celiac disease. Based on this result we could suggest a routine screening test for celiac disease in all children with β- thalassemia minor.
Keywords: Celiac, Children, Thalassemia minor, TTG IgA
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.