Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 7 (4); 25 December, 2017
Research Paper
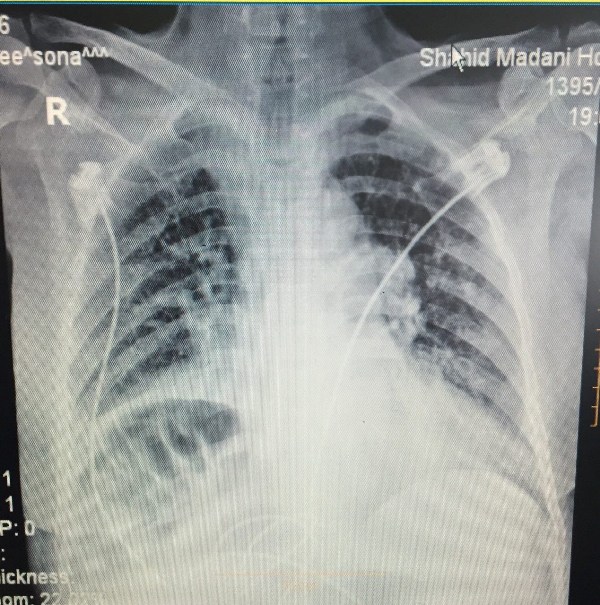
Chilaiditi syndrome: A Case presented with peritonitis symptoms.
Hejazi M-E, Seifar F, Mohammadpour H, Salmannezhad Khorami F, Namvar L, Hejazi Y. Hajibonabi F.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(4): 35-41, 2017; pii:S2252043017000008-7
Abstract
We reported a patient affected by the Chilaiditi’s syndrome, the interposition of the small or large intestine between liver and right hemi diaphragm which is a rare asymptomatic condition. A 70-year-old female with a history of respiratory failure was presented with abdominal pain characteristic for peritonitis. The radiologic findings and symptoms resolved after conservative management with bowl rest and decompression. In conclusion, conservative treatment in addition to radiologic findings were representative of Chilaiditi syndrome.
Keywords: Chilaiditi syndrome, Abdomen, Chilaiditi sign
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
Gingko biloba Leaf Extract Mitigates Chlorpyrifos-Induced Oxidative Stress in Albino Rat.
Nuhu AA, Abdulrazak S, Yashim ZI.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 7(4): 42-47, 2017; pii:S2252043017000009-7
Abstract
Gingko biloba leaf extract is one of the most popular botanical drug preparations in the world due to its reliable biological activities. The present study was carried out to evaluate the in vivo prophylactic and therapeutic antioxidant activities of Gingko biloba leaf extract in rats experimentally exposed to chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress through evaluating glutathione concentrations, malondialdehyde concentration, superoxide dismutase, and catalase activities. Exactly 35 adult albino rats randomly divided into 7 groups of 5 animals each were used for this study. The results indicated that pre-treatment with Gingko biloba leaf extract significantly (P˂0.05) increased the activity of superoxide dismutase, and level of glutathione and decreased serum malondialdehyde concentration compared to groups pre-treated with vitamin E. Similarly, pre treatment with Gingko biloba leaf extract significantly (P ˂ 0.05) increased the activity of superoxide dismutase and level of glutathione and lowered serum malondialdehyde concentration when compared to post treatment with Gingko biloba leaf extract. However, catalase activity was not significantly affected by the treatments. The results showed that the extract has both prophylactic and therapeutic activities, but its prophylactic activity was more expressed than the therapeutic activity. Also, the prophylactic antioxidant activity of the extract was more than that of vitamin E, a reference antioxidant in this study which is a fat-soluble vitamin with powerful antioxidant properties. These results further justify the use of Gingko biloba leaf extract in both medical and ethnomedical practices for the treatment of various disorders.
Keywords: Antioxidants, Catalase, Chlorpyrifos, Gingko biloba leaf extract, Glutathione, Malondialdehyde, Superoxide dismutase, Vitamin E
[Full text-PDF] [XML]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.